Table of contents
Related articles
Introduction
Request Fulfilment is an ITIL® process that is part of the Service Operation Phase:
Definitions
Please consult "Request Fulfilment" section of the ITIL® Glossary.
Objectives
Request fulfilment process objectives are:
- Provide a channel for users to request and receive standard services for which a predefined authorization and qualification process exists
- Provide information to users and customers about the availability of services and the procedure for obtaining them
- Source and deliver the components of requested standard services
- Assist with generaal information, complaints or comments
Scope
The process needed to fulfil a request will vary depending upon exactly what is being requested, but can usually be broken down into a set of activities that have to be performed. For each request, these activities should be documented into a request model.
There is a significant difference between a service request and an incident - an incident is an unplanned event, whereas a service request is usually something that can and should be planned.
It is up to each organization to decide and document service requests to be managed in the Request Fulfilment process, and those that must be managed through other processus, such as Change Management.
Value
- Provide quick and effective access to standard services used by end-users to improve their productivity or the quality of business services
- Reduce the bureaucracy involved in requesting and receiving access to existing or new services, thus also reducing the costs of providing these services
- Increase the level of control over requested services through a centralized fulfilment function
Basic concepts
Request models
Some service requests will occur frequently and will require handling consistently in order to mee agreed service levels. Creation of predefined request models, including a set of activities, establish a standard in requests execution.
Menu Selection
Ideally, users should be offered a "menu"-type selection via a web-based interface or request portal so that they can select and input details of service requests from a predefined list. In this way, users can be informed of execution targets that are defined in the service level agreements.
Request status tracking
Requests should be tracked throughout their lifecycle to support proper handling and reporting on the status of requests. Within the request fulfilment system, status codes may be linked to requests to indicate where they are in relation to the lifecycle. By exemple: new, waiting for approval, in process, refused, canceled, completed, etc.
Prioritizing requests
All service requests should follow a standard set of criteria for assessing their priority. This could be done by considering request impact and urgency, in a similar manner as described for Incident Management.
Escalating requests
It may be necessary to escalate requests to resolve certain situations or take further actions that are not part of the standard set of fulfilment activities. We could refer to a request misrouted to the wrong group, a SLA for fulfilling a request may be in jeopardy, a user disagrees that the request has been fulfilled to his entire satisfaction, a request has been used in lieu of a more complicated requirement.
Approval
The approval of a request can be required for several reasons. This could be for obtaining approval prior a hardware or software acquisition, or approval prior granting access to IT assets.
The cost of a standard service request delivery can be fixed or, for other types of request, estimated for the sake of recharging, if this is applied in the organization.
Coordination of fulfilment activities
Request Fulfilment activity will depend upon the nature of the service request. Some simpler requests may be completed by the Service Desk, acting as first-line support, while others will have to be forwarded to specialist groups or suppliers for fulfilment. The Service Desk should monitor and chase progress and keep users informed throughout, regardless of the actual fulfilment source.
Closure
When the service request is completed, it is referred back to the Service Desk for closure. The Service Desk should check to se whether the user is satisfied with the outcome.
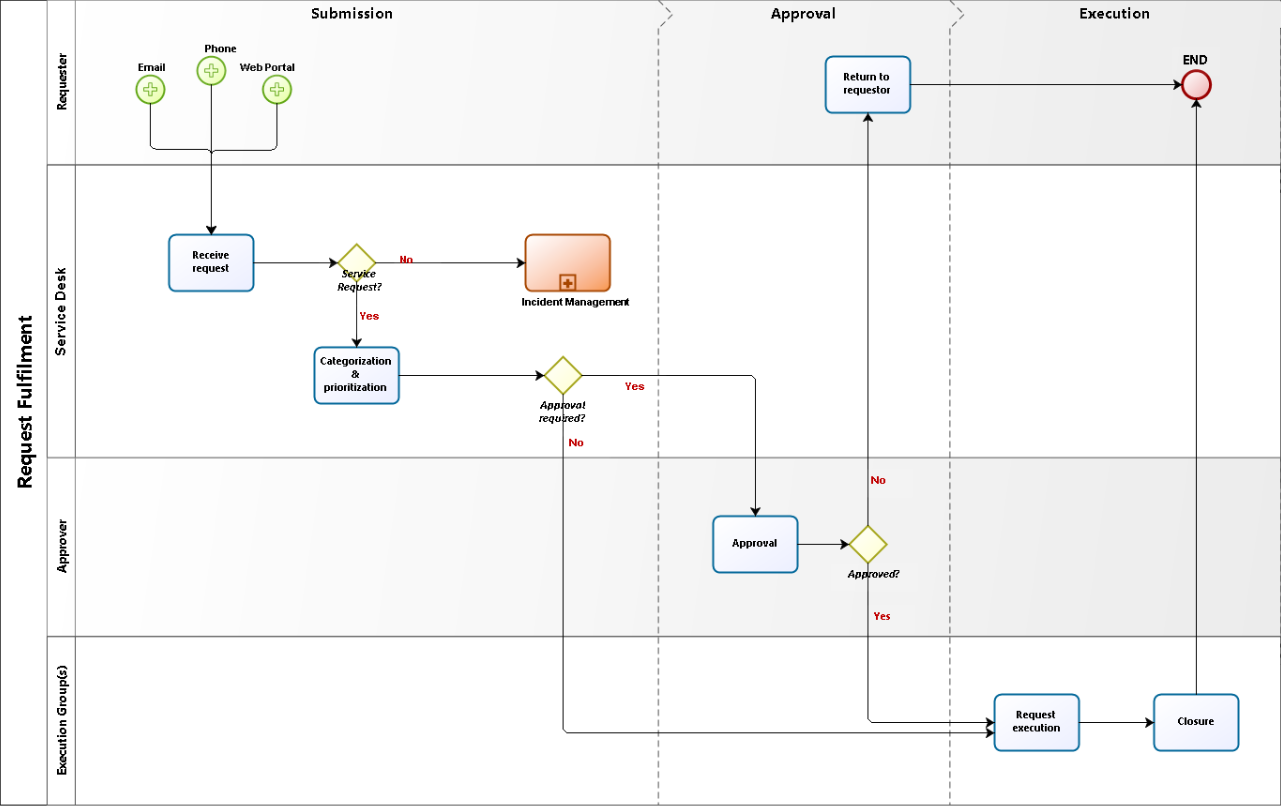
Process and activities
Thank you, your message has been sent.
